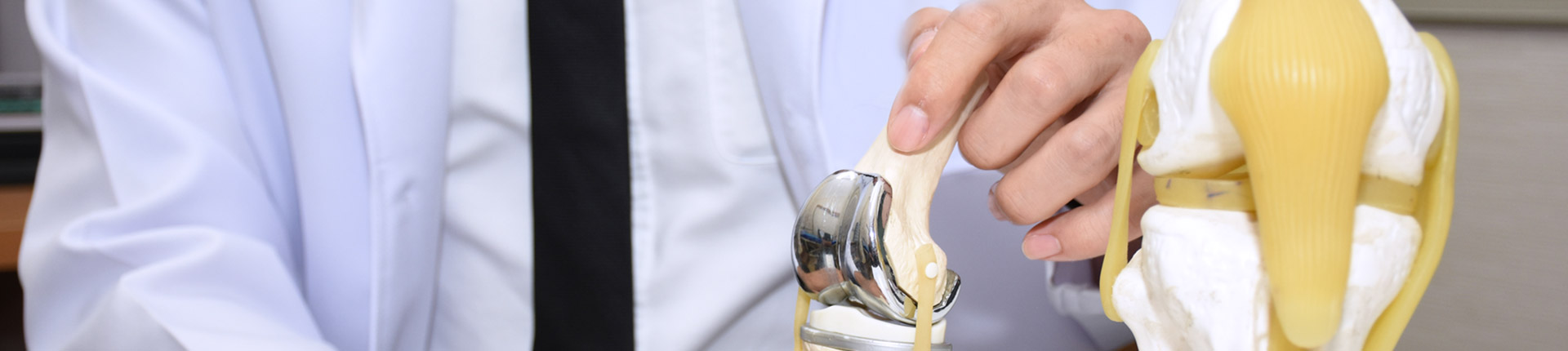
Joint Replacement Patients
When to call your surgeon
and symptoms

When to call your surgeon
and symptoms
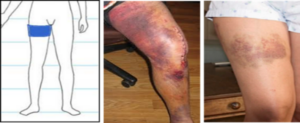
Knee Replacement Patients: A tourniquet was placed on your upper thigh to reduce blood loss during surgery. Bruising from the tourniquet is normal and expected.
Changes in daily routine, short-term reductions in appetite and mobility, as well as narcotic pain medication can contribute to an increased risk for constipation.
Follow your surgeon’s instructions for constipation management and prevention.
Although risks are low for postoperative infections, the risk remains. A prosthetic joint could possibly attract bacteria from an infection located in another part of your body.
If you sustain an injury such as a deep cut or puncture wound, you should clean it as best you can, put a dressing or adhesive bandage on it, and notify your doctor. The closer the injury is to your prosthesis, the greater the concern.
Occasionally, antibiotics may be needed. Superficial scratches may be treated with topical antibiotic ointment. Notify your doctor if any area is painful or red.
Follow the guidelines in the next section below to prevent blood clots from forming.
Surgery may cause the blood to slow and clot in veins of the legs. If a clot occurs, you may need to be admitted to the hospital to receive blood thinning medication. Blood clots can form in either of your legs.
Blood clots after surgery can cause serious problems. However, there are steps that can be taken to help prevent them:
Report any anticoagulant-related side effects such as large amount of bleeding immediately!
There are many different types of blood thinning medications. Some are oral (by mouth) while others require injections. Your doctor will select the type of medication that is best for you.
When taken according to your surgeon’s instructions, blood thinners are generally safe and effective. However, in some cases, there may be warning signs that prompt treatment is needed.
If you fall, have a traumatic injury, or if you experience any of the following, call your surgeon immediately. DO NOT WAIT AND HOPE THE SYMPTOMS GO AWAY.
Certain medications, foods and activities can interact negatively and interfere with blood thinners. It is important to take proper steps to avoid any potential complications.